- Home >> News >> Research Progress
Efficient Enzyme Cocktail from Penicillium Consortium to Enhance Lignocellulose Biodegradation
Lignocellulosic biomass is the most abundant feedstock in production of bio-based fuels and materials. In order to achieve high conversion efficiency, enzyme cocktail has been assessed by numerous studies as a powerful tool to allocate diverse specific activities in one matrix.
A recent study from the Guangzhou Institute of Energy Conversion of the Chinese Academy of Sciences reported an efficient cellulase cocktail produced by co-cultivation of several Penicillium strains with lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases (LPMOs) producing strains, achieving excellent hydrolysis yield of pretreated poplar materials.
Fermentation of fungal consortium is an effective approach to improve the yield of enzymes and coordinate the proportion of enzyme system through the synergistic effect of mutual benefit and symbiosis among multiple strains. This study investigated co-fermentation of four kinds of Penicillium strains with Thermoascus aurantiacus and Neurospora crassa by mixture design methodology.
Based on the commercial cellulase as benchmark, comparative analysis of the enzyme components, activities and the strains transcriptome provided a comprehensive insight that the enzyme cocktail from Penicillium consortium presented superior expression on diverse Glycoside Hydrolases (GHs), Glycosyl Transferases (GTs), Polysaccharide Lyases (PLs) and other auxiliary enzymes, accelerating the chemical bonds breaking of hemicellulose and cellulose fractions.
In order to improve synergistic enzyme actions, a new formulation was developed by blending fermented enzyme cocktail with commercial cellulase in an appropriate proportion. The pretreated poplar was successfully hydrolyzed to release glucose at yield of 88%, equivalent to 32% increase compared to using commercial cellulase alone.
Prof. Qi Wei, the principle investigator, said the self-developed fungal consortium and enzyme formulation have good potent to be applied in industry as a green and powerful tool, to enhance lignocellulose biodegradation and consequently reduce enzyme cost. It is important for sustainable development of agriculture and forest wastes biorefinery, to produce biofuels and materials.
The techno-economic efficiency is the most critical consideration for upscaling biotechnology, he said.
The paper was published online in Chemical Engineering Journal entitled“Enhancement of an efficient enzyme cocktail from Penicillium consortium on biodegradation of pretreated poplar” (DOI: doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.139352).
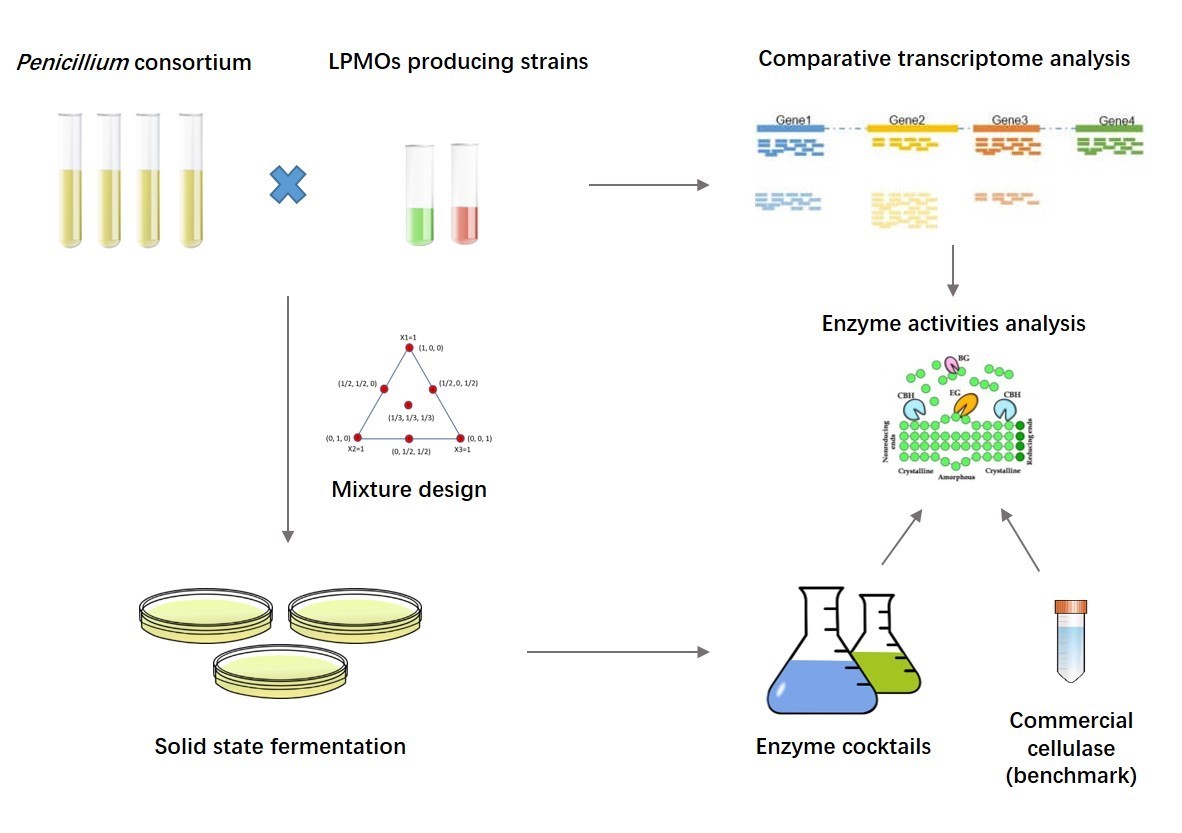
Efficient enzyme cocktail from Penicillium consortium (Image by HU Yunzi)
Contact:
Dr. QI Wei
Guangzhou Institute of Energy Conversion, Chinese Academy of Sciences
(http://english.giec.cas.cn/)
Guangzhou 510640, China
Tel: 86-20-37029685
E-mail: qiwei@ms.giec.ac.cn
