- Home >> News >> Research Progress
Novel Progress in the Study of the Evolution of Ice Particles During Subcooling Release by GIEC
Recently, the research team of Prof. FENG Ziping, from Guangzhou Institute of Energy Conversion (GIEC), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), has achieved innovative research outcomes on the evolution of ice particles during subcooling release. The details of this study have been published in International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer under the title of “Investigation on the evolution of ice particles and ice slurry flow characteristics during subcooling release”.
Ice slurry is a binary fluid consisting of distributed ice particles and water/aqueous solution. It features decent heat transfer and distinguishing hydraulic characteristics, presenting significant advantages in the storage and transport of cold energy. Controllable subcooling phase change technology is the key to fulfilling efficient and continuous ice slurry generation. The growth of ice particles driven by subcooling in the liquid phase is the innovation and highlight of this study.
As one of the important aspects of controlled subcooling phase change, the present research outcomes are expected to effectively address the problem of ice clogging during ice slurry generation, and facilitate the design of ice slurry generators.
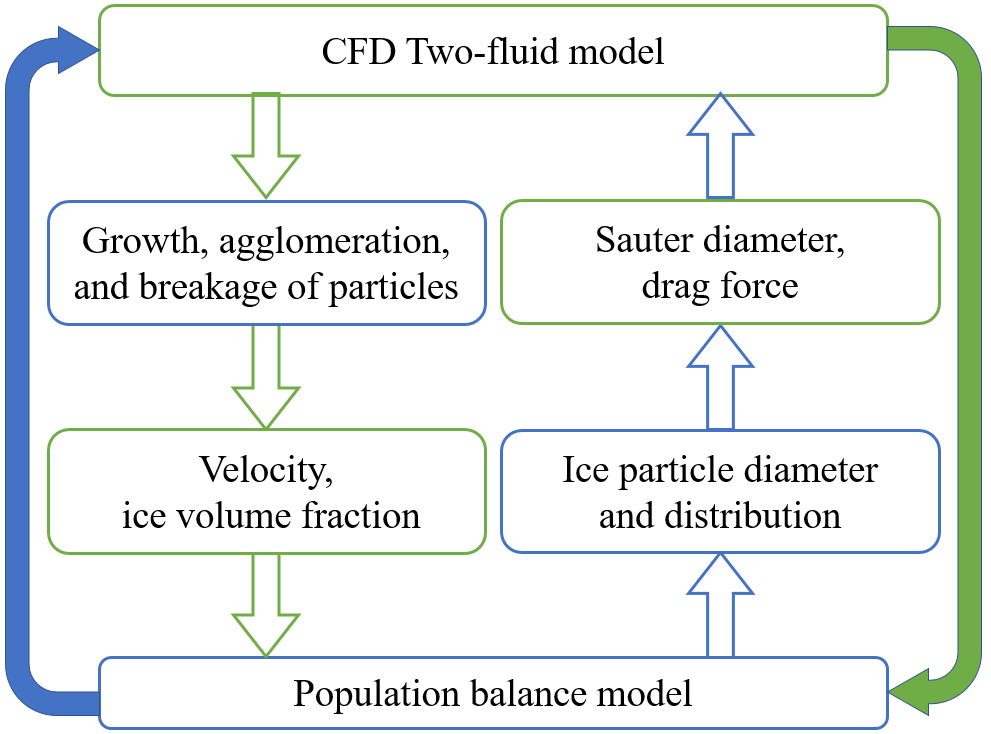
Figure 1.The couple of CFD model and PBM(Image by Qun Du)
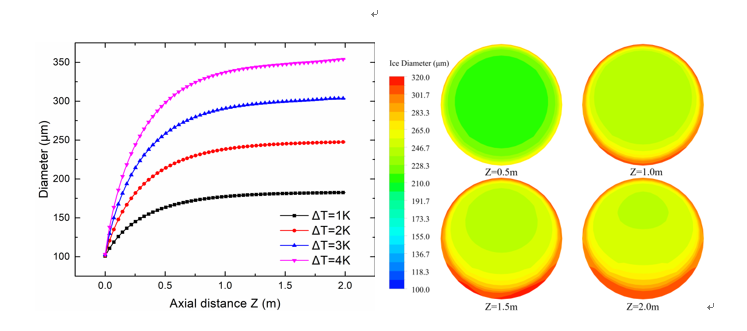
Figure 2.Evolution of ice particles in a horizontal straight pipe(Image by Qun Du)
Contact:
Dr. FENG Ziping
Guangzhou Institute of Energy Conversion, Chinese Academy of Sciences
(http://english.giec.cas.cn/)
Guangzhou 510640, China
Tel: 86-20-37244145
E-mail: fengzp@ms.giec.ac.cn
